Active Directory (AD) is Microsoft’s proprietary directory service. It runs on Windows Server and allows administrators to manage permissions and access to network resources. Active Directory stores data as objects. An object is a single element, such as a user, group, application or device, e.g., a printer. Objects are normally defined as either resources, such as printers or computers, or security principals, such as users or groups.
The main service in Active Directory is Domain Services (AD DS), which stores directory information and handles the interaction of the user with the domain. AD DS verifies access when a user signs into a device or attempts to connect to a server over a network. AD DS controls which users have access to each resource, as well as group policies. For example, an administrator typically has a different level of access to data than an end user.
Active Directory Domain Services uses a tiered layout consisting of domains, trees and forests to coordinate networked elements.
- A domain is a group of objects, such as users or devices, that share the same AD database. Domains have a domain name system(DNS) structure.
- A tree is one or more domains grouped together. The tree structure uses a contiguous namespace to gather the collection of domains in a logical hierarchy. Trees can be viewed as trust relationships where a secure connection, or trust, is shared between two domains. Multiple domains can be trusted where one domain can trust a second, and the second domain can trust a third. Because of the hierarchical nature of this setup, the first domain can implicitly trust the third domain without needing explicit trust.
- A forest is a group of multiple trees. A forest consists of shared catalogs, directory schemas, application information and domain configurations. the schema defines an object’s class and attributes in a forest. In addition, global catalog servers provide a listing of all the objects in a forest. According to Microsoft, the forest is Active Directory’s security boundary.
- Organizational Units (OUs) organize users, groups and devices. Each domain can contain its own OU. However, OUs cannot have separate namespaces, as each user or object in a domain must be unique. For example, a user account with the same username cannot be created.
- Containers are similar to OUs, but Group Policy Objects (GPO) cannot be applied or linked to container objects

- Install AD DS
- Configure new DC
- Join in Domain from Client host
- Add User Accounts
- Add Group Accounts
- Add Organizational Unit
- Add Computer Accounts
Install AD DS
Step 1: Run Server Manager and Click Add roles and features and click Next on first page
Step 2: Select Role-based or feature-based installation.

Step 3: Select a Host which you’d like to add services.

Step 4: Check a box Active Directory Domain Services.
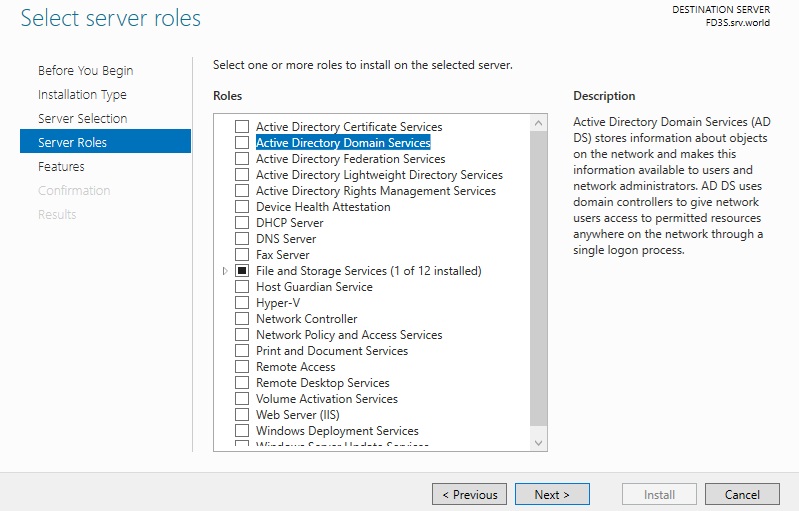
Step 5: Additional features are required to add AD DS. Click Add Features button.

Step 6: Click Next button.

Step 7: Click Next button.

Step 8: Click Install button.

Step 9: After finishing Installation, click Close button.

Configure new DC
Step 1: Run Server Manager and click AD DS, next, on the screen below, Click More… link which is upper-right on the left pane.

Step 2: Click Promote this server to domain… link.

Step 3: Check a box Add a new forest and input any Domain name you’d like to set for Root domain name field.

Step 4: Select Forest functional level and Domain functional level. This example shows to select Windows Server 2016 both. Furthermore, Set any password for Directory Services Restore Mode.

Step 5: Click Next button.

Step 6: Input NetBIOS name you’d like to set.

Step 7: Specify Database folder or Log folder and so on. It’s Ok to keep default if you don’t have specific requirements.

Step 8: Check the contents you configured and click Next button.

Step 9: Click Install button. After finishing it, System will restart automatically.

Step 10: After restarting System, logon name is changed as Domain name/ User name.

Step 11: It’s OK if logged in normally.
Join in Domain from Client host
Join in Active Directory Domain from Other Windows Client Hosts. This example is based on Windows 10.
Step 1: Open Network settings and then, select TCP/IPv4 and click Properties button.
Control Panel\Network and Internet\Network Connections
Change to DNS settings to refer Active Directory Host.

Step 2: Open System and click Change settings link which is lower-right.

Step 3: Move to Computer Name tab and click Change button.

Step 4: Check a box Domain and input domain name and next, click OK button.

Step 5: Authentication is required, authenticate with a domain User in Active Directory.

Step 6: After successful authentication, Welcome message is shown like follows. Restart the Computer once.

Step 7: On the logon screen after restarting Computer, click another user to switch Domain user to logon. Authenticate with a Domain user you added.
Step 8: You have just Logon to Active Directory Domain.
Add User Accounts
Step 1: Run Server Manager and click Tools -> Active Directory Users and Computers.

Step 2: Right-Click Users on left tree and select New -> User.

Step 3: Input Username and Logon name for a new user.

Step 4: Set initial password for a new User.

Step 5: Check contents you set and click Finish button.

Step 6: A new user is just added.
Add Group Accounts
Step 1: Run Server Manager and open Tools -> Active Directory Users and Computers, next, Click with right button Users on left tree and select New -> Group.

Step 2: Input a Group name you’d like to add.
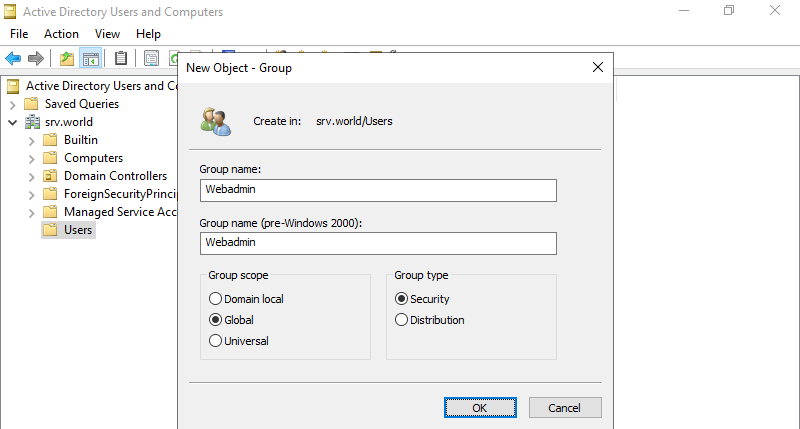
Step 3: A new Group is just added.

Step 4: For adding users in a Group,
Right Click the Group and Open Properties.

Step 5: Move to Member tab and Click Add button.

Step 6: Input a user you’d like to add to this Group and Click OK.

Step 7: Confirm the Properties of the user you added to the Group.

Add Organizational Unit
Step 1: Run Server Manager and open Tools -> Active Directory Users and Computers, next, right-Click your domain name on the left tree and select New -> Organizational Unit.
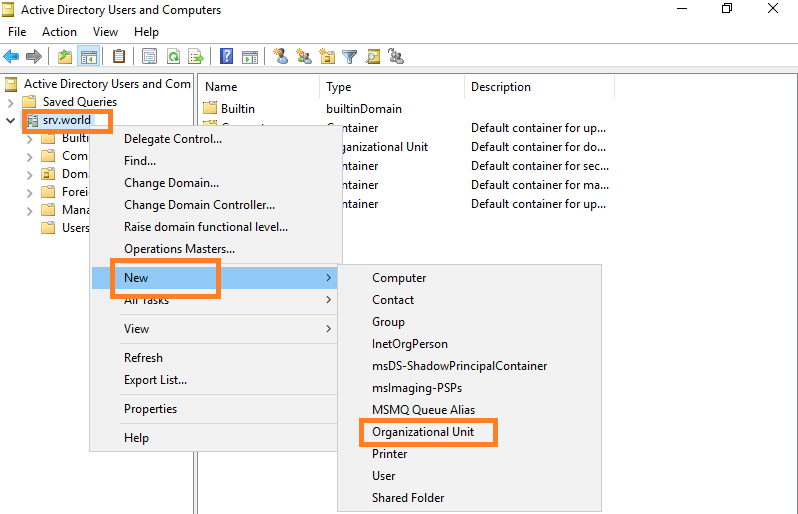
Step 2: Set any name for OU.

Step 3: A new Organizational Unit is just created.

Step 4: It’s possible to configure hierarchical design for Organizational Unit.

Add Computer Accounts
By default settings, if you don’t add Computer Accounts by yourself, Computers can join in Domain with common users rights who don’t have admin privileges. So if you’d like to limit authentication users when computers join to Domain, Add Computer Accounts beforehand.
Step 1: Run Server Manager and open Tools -> Active Directory Users and Computers, next, right-Click Computers on the left tree and select New -> Computer.

Step 2: Input a new Computer name. By default, the users when used for authentication to join in Domain are Domain Admins group users, but if you’d like to change it, it’s possible to change it on User or group field.

Step 3: A new Computer is just added.





