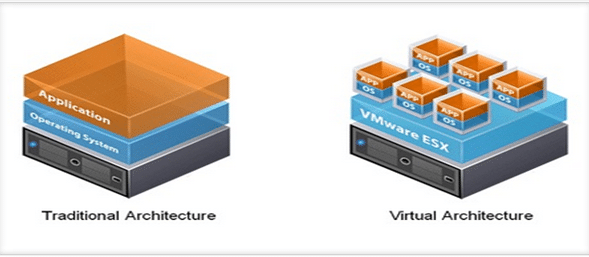
Virtualization is a technology that helps us to install different Operating Systems on a hardware. They are completely separated and independent from each other. In Wikipedia, you can find the definition as – “In computing, virtualization is a broad term that refers to the abstraction of computer resources.
Virtualization hides the physical characteristics of computing resources from their users, their applications or end users. This includes making a single physical resource appear to function as multiple virtual resources. It can also include making multiple physical resources appear as a single virtual resource.

Types of Virtualization
Term virtualization is widely applied to a number of concepts, some of which are described below:
- Server Virtualization
- Client & Desktop Virtualization
- Services and Applications Virtualization
- Network Virtualization
- Storage Virtualization
1. Server Virtualization
It is virtualizing your server infrastructure where you do not have to use any more physical servers for different purposes.
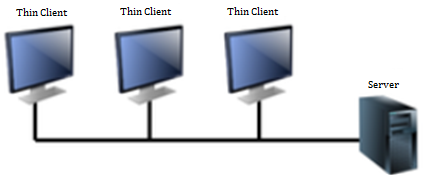
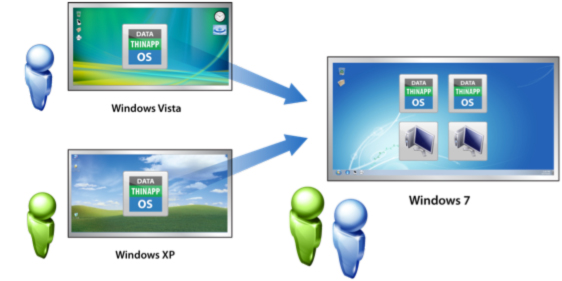
2. Client & Desktop Virtualization
This is similar to server virtualization, but this time is on the user’s site where you virtualize their desktops. We change their desktops with thin clients and by utilizing the datacenter resources.
3. Services and Applications Virtualization
The virtualization technology isolates applications from the underlying operating system and from other applications, in order to increase compatibility and manageability. For example – Docker can be used for that purpose.
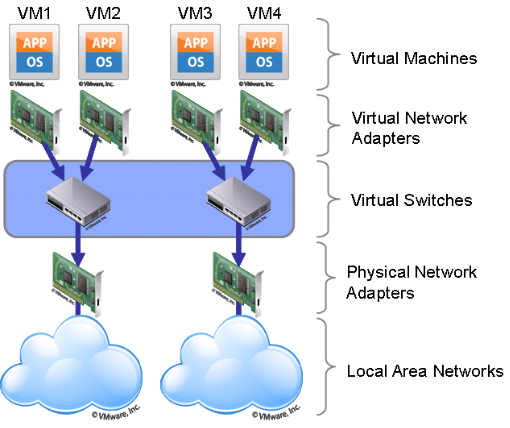
4. Network Virtualization
It is a part of virtualization infrastructure, which is used especially if you are going to visualize your servers. It helps you in creating multiple switching, Vlans, NAT-ing, etc.
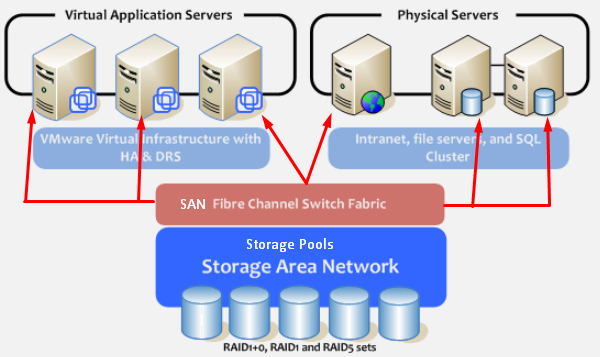
5. Storage Virtualization
This is widely used in datacenters where you have a big storage and it helps you to create, delete, allocated storage to different hardware. This allocation is done through network connection. The leader on storage is SAN.