The rm command is used to delete files and directories. It is important to keep in mind that deleted files and directories do not go into a “trash can” as with desktop-oriented operating systems. When a file is deleted with the rm command, it is almost always permanently gone.
rm [OPTIONS] FILE
Without any options, the rm command is typically used to remove regular files:
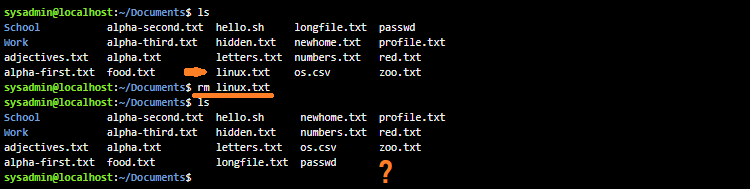
The rm command will ignore directories that it’s asked to remove; to delete a directory, use a recursive option, either the -r or -R options. Just be careful since these options are “recursive”, this will delete all files and all subdirectories:
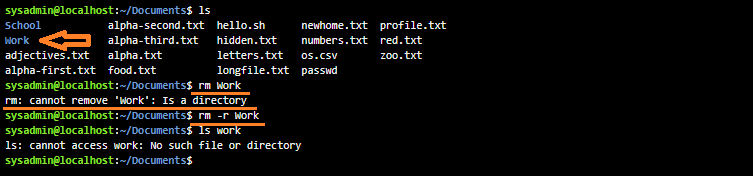
Note: Permissions can have an impact on file management commands, such as the rm command.To delete a file within a directory, a user must have write and execute permission on a directory. Regular users typically only have this type of permission in their home directory and its subdirectories.





