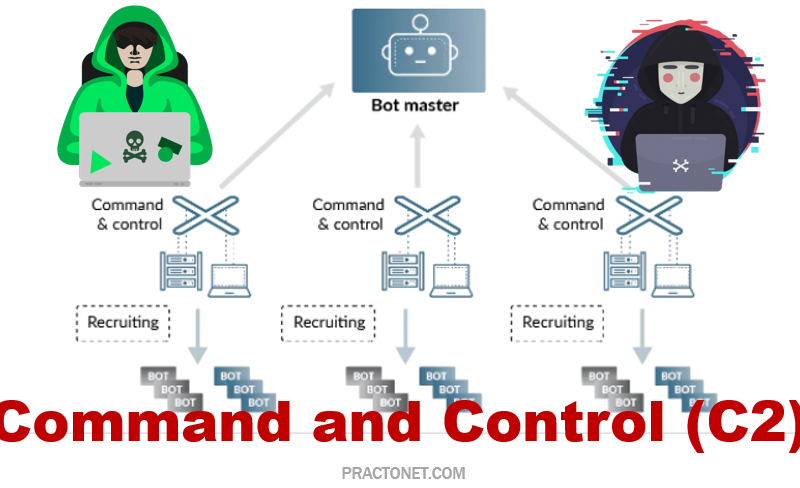
A “Firewall” is one of the most popular computer and network security devices that professionals use to protect their enterprise IT assets and networks. Just like a fire-resistant door in buildings which protects rooms from a possible fire and stops the spreading of flames within the building, the security firewall has a similar function to prevent malicious packets and traffic from entering and harming your protected computer assets.
Network based Firewall
A network-based firewall controls traffic going in and out of a network. It does this by filtering traffic based on firewall rules and allows only authorized traffic to pass through it. Most organizations include at least one network-based firewall at the boundary between their internal network and the Internet.
The network-based firewall is usually a dedicated system with additional software installed to monitor, filter, and log traffic. A network-based firewall would have two or more network interface cards (NICs) and all traffic passes through the firewall. Many network-based firewalls are dedicated servers or appliances.
Host based Firewall
A host-based firewall is a piece of firewall software that runs on an individual computer or device connected to a network. These types of firewalls are a granular way to protect the individual hosts from viruses and malware, and to control the spread of these harmful infections throughout the network.
Some companies use host-based firewalls in addition to perimeter-based firewalls in order to enhance internal security. For example, some of the malware attacks that may get past a perimeter firewall can be stopped at the individual device or workstation, using a host-based firewall. A host-based firewall setup can also be simpler for some users. The host-based firewall can also be configured to the particular computer, where customization can make the firewall more effective.
A classic example of host firewall is the Windows Firewall which comes by default in all Windows Operating Systems.
Network based Firewall vs. Host based Firewall
| Characteristics | Network based Firewall | Host based Firewall |
|---|---|---|
| Terminology | Firewall filters traffic going from Internet to secured LAN and vice versa | A host firewall is a software application or suite of applications installed on a singular computer |
| Placement | At the Perimeter or border of the network like Internet handoff point to address the unauthorized access from the entry/exit point. | Placed at end Host systems and will be in a way, 2nd line of defence if unauthorized traffic has not been blocked by Network based firewall. |
| Hardware/Software based | Hardware based | Software based |
| Functions at | Network Level | Host Level |
| Internal Protection | For end host to end host communication in same VLAN , Network Firewall does not provide security | For end host to end host communication in same VLAN, Host based Firewall provides security control and protection. |
| Network Protection | Strong defence barrier compared with host-based. Infact Network Firewalls are hardened enough leaving very less space for attacker to play. | Limited defence barrier compared to Network firewalls |
| Scalability | Easy to scale since increase in number of users in LAN triggers more bandwidth requirement and rightly sized Firewall considering future growth does not require much of effort to accommodate high bandwidth. | More effort required to scale in terms of more installations & maintenance on each device when number of hosts increase |
| Maintenance | Manpower may be shared and limited since only 1 or 2 sets of Network Firewall need to be managed | Dedicated IT team required to monitor and maintain and update Host based Firewall on each end device |
| Skillset | Setup requires highly skilled resources with good understanding of Security devices | Skillset of basic Hardware/software understanding and program installation |
| Cost | Lower when comes to large enterprise | Higher when it comes to large enterprises |
| How easy to bypass | Network firewalls can’t be bypassed by attackers. | Easier to bypass. If the attacker compromises the host via an exploit, the firewall can be turned-off by the hacker. |