Cloud Computing architecture comprises of many cloud components, which are loosely coupled. We can broadly divide the cloud architecture into two parts:
- Front End
- Back End
Each of the ends is connected through a network, usually Internet. The following diagram shows the graphical view of cloud computing architecture:
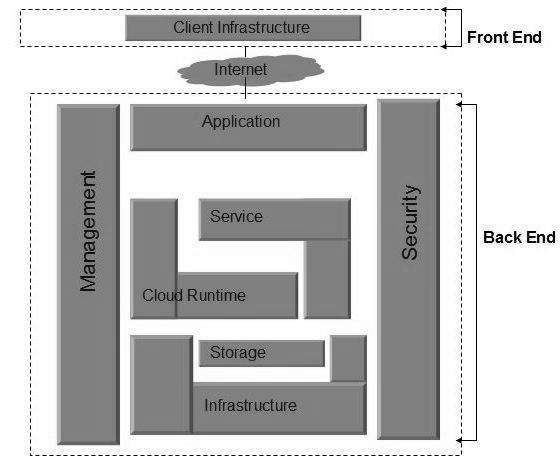
Front End
The front end refers to the client part of cloud computing system. It consists of interfaces and applications that are required to access the cloud computing platforms, Example – Web Browser.
Back End
The back End refers to the cloud itself. It consists of all the resources required to provide cloud computing services. It comprises of huge data storage, virtual machines, security mechanism, services, deployment models, servers, etc.
Cloud infrastructure consists of servers, storage devices, network, cloud management software, deployment software, and platform virtualization.
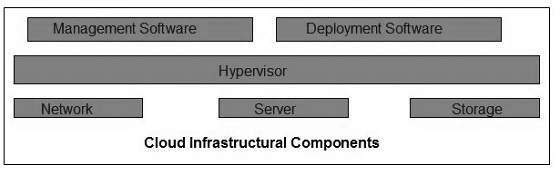
Hypervisor
Hypervisor is a firmware or low-level program that acts as a Virtual Machine Manager. It allows to share the single physical instance of cloud resources between several tenants.
Management Software
It helps to maintain and configure the infrastructure.
Deployment Software
It helps to deploy and integrate the application on the cloud.
Network
It is the key component of cloud infrastructure. It allows to connect cloud services over the Internet. It is also possible to deliver network as a utility over the Internet, which means, the customer can customize the network route and protocol.
Server
The server helps to compute the resource sharing and offers other services such as resource allocation and de-allocation, monitoring the resources, providing security etc.
Storage
Cloud keeps multiple replicas of storage. If one of the storage resources fails, then it can be extracted from another one, which makes cloud computing more reliable.





